Жасанды интеллектті ойындар есебінде эвристикалық функцияларды қолдану тақырыбында мәліметтер бар ма?
өтініш жауап жазыңыздаршы.Қатты керек болып жатыр."Игра в 8" ойыны пролог т3л3нде программасы бар болса отинем жибериндерши!!!рахмет.
Ақшолпан 2014-04-10 18:42:33
Жауаптар 4
ЖУГЕРІ ҚУЫРМАСЫ
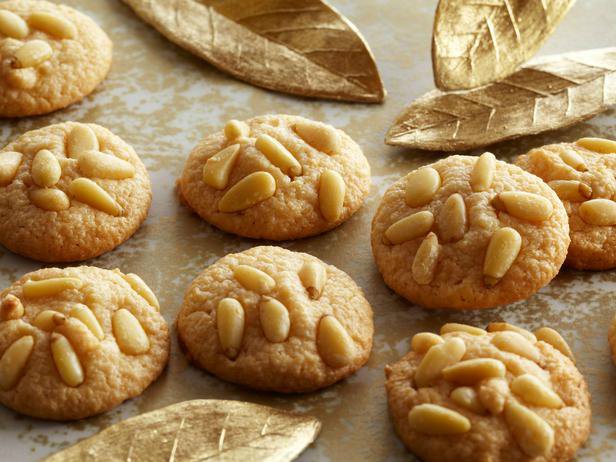

Жұмыртқа мен қантты 40-50 градусқа дейін қыздырып, шайқау керек. Оны шайқай отырып бөлме температурасына дейін салқындатады.
АТ САЙЫСЫ
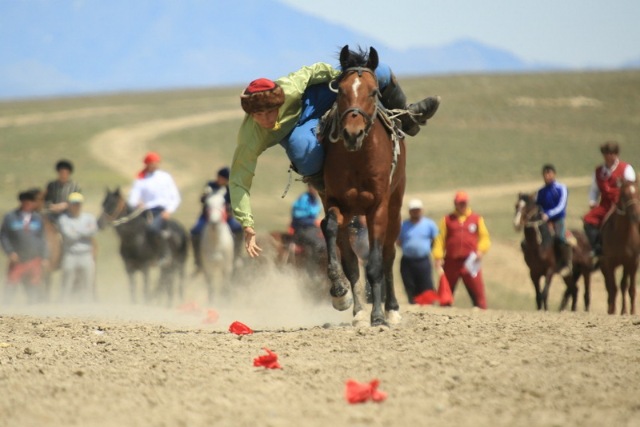

Қазақ халқында Ат сайысына жататын бәйге, ат омарластыру, аударыспақ, жорға жарыс, көкпар, күміс алу, қыз қуу, қыз жарыс, сайысу т.б. ойындар бар.
КЕНДІ ҚАЛАЙ ӨНДІРЕДІ
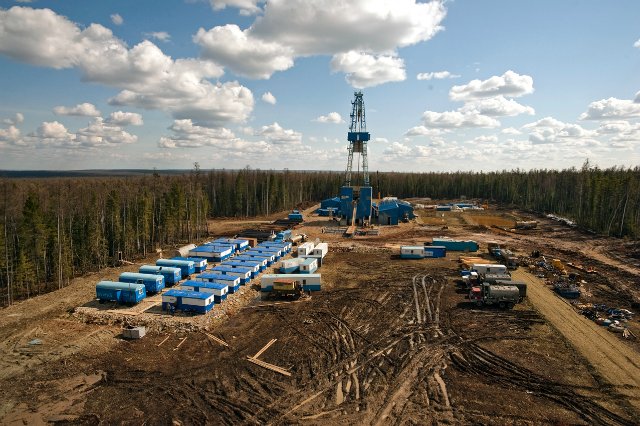

Біз әуелі кен байлығы, яғни қазба байлық дегеніміз не екенін білейік. Біз өмір сүріп жатқан Жер, оның қыртысы алуан түрлі топырақтардан, тастардан, т.б. нәрселерден тұратынын білеміз. Олардың барлығы кен байлығына жатпайды.
ІЛЕ АЛАТАУЫ ҰЛТТЫҚ ТАБИҒАТ САЯБАҒЫ
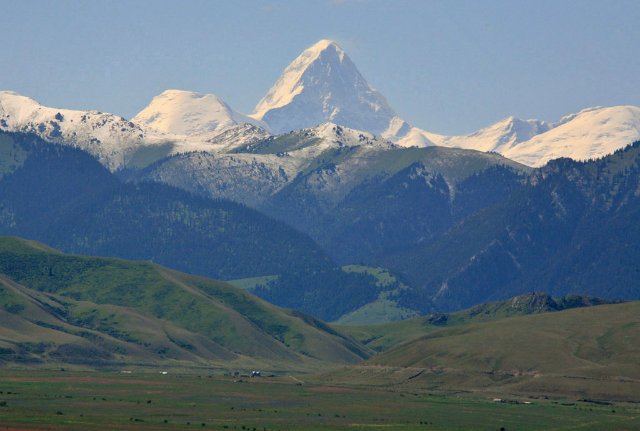

Іле Алатауы ұлттық табиғат саябағы - Алматы қаласы іргесіндегі Алматы тау жотасында орналасқан. Саябақ табиғи кешендерді, жануарлар мен өсімдіктердің сирек кездесетін түрлерін қорғау мақсатында 1996 жылы құрылған.

Ақшолпан
Фархат,кешириниз программаның domains және predicates clauses бөлімдерінде не жазу керек?
Ақшолпан
рахмет көп.
Айнаш
автор Сошникове кітаптын аты (Парадигма логического программирования) бүл есептын шешімі бар
Фархат
Шешімді
% Problem-specific procedures for the eight
% puzzle, to be used in best-first search
/* Problem-specific procedures for the eight puzzle
Current situation is represented as a list of positions of the tiles,
with first item in the list corresponding to the empty square.
Example:
This position is represented by:
3 1 2 3
2 8 4 [2/2, 1/3, 2/3, 3/3, 3/2, 3/1, 2/1, 1/1, 1/2]
1 7 6 5
1 2 3
"Empty' can move to any of its neighbours which means
that "empty' and its neighbour interchange their positions.
*/
% s( Node, SuccessorNode, Cost)
s( [Empty | Tiles], [Tile | Tiles1], 1) :- % All arc costs are 1
swap( Empty, Tile, Tiles, Tiles1). % Swap Empty and Tile in Tiles
swap( Empty, Tile, [Tile | Ts], [Empty | Ts] ) :-
mandist( Empty, Tile, 1). % Manhattan distance = 1
swap( Empty, Tile, [T1 | Ts], [T1 | Ts1] ) :-
swap( Empty, Tile, Ts, Ts1).
mandist( X/Y, X1/Y1, D) :- % D is Manhhattan dist. between two squares
dif( X, X1, Dx),
dif( Y, Y1, Dy),
D is Dx + Dy.
dif( A, B, D) :- % D is |A-B|
D is A-B, D >= 0, !
;
D is B-A.
% Heuristic estimate h is the sum of distances of each tile
% from its "home' square plus 3 times "sequence' score
h( [Empty | Tiles], H) :-
goal( [Empty1 | GoalSquares] ),
totdist( Tiles, GoalSquares, D), % Total distance from home squares
seq( Tiles, S), % Sequence score
H is D + 3*S.
totdist( [], [], 0).
totdist( [Tile | Tiles], [Square | Squares], D) :-
mandist( Tile, Square, D1),
totdist( Tiles, Squares, D2),
D is D1 + D2.
% seq( TilePositions, Score): sequence score
seq( [First | OtherTiles], S) :-
seq( [First | OtherTiles ], First, S).
seq( [Tile1, Tile2 | Tiles], First, S) :-
score( Tile1, Tile2, S1),
seq( [Tile2 | Tiles], First, S2),
S is S1 + S2.
seq( [Last], First, S) :-
score( Last, First, S).
score( 2/2, _, 1) :- !. % Tile in centre scores 1
score( 1/3, 2/3, 0) :- !. % Proper successor scores 0
score( 2/3, 3/3, 0) :- !.
score( 3/3, 3/2, 0) :- !.
score( 3/2, 3/1, 0) :- !.
score( 3/1, 2/1, 0) :- !.
score( 2/1, 1/1, 0) :- !.
score( 1/1, 1/2, 0) :- !.
score( 1/2, 1/3, 0) :- !.
score( _, _, 2). % Tiles out of sequence score 2
goal( [2/2,1/3,2/3,3/3,3/2,3/1,2/1,1/1,1/2] ). % Goal squares for tiles
% Display a solution path as a list of board positions
showsol( [] ).
showsol( [P | L] ) :-
showsol( L),
nl, write( '---'),
showpos( P).
% Display a board position
showpos( [S0,S1,S2,S3,S4,S5,S6,S7,S8] ) :-
member( Y, [3,2,1] ), % Order of Y-coordinates
nl, member( X, [1,2,3] ), % Order of X-coordinates
member( Tile-X/Y, % Tile on square X/Y
[' '-S0,1-S1,2-S2,3-S3,4-S4,5-S5,6-S6,7-S7,8-S8] ),
write( Tile),
fail % Backtrack to next square
;
true. % All squares done
% A best-first search program.
% bestfirst( Start, Solution): Solution is a path from Start to a goal
bestfirst( Start, Solution) :-
expand( [], l( Start, 0/0), 9999, _, yes, Solution).
% Assume 9999 is greater than any f-value
% expand( Path, Tree, Bound, Tree1, Solved, Solution):
% Path is path between start node of search and subtree Tree,
% Tree1 is Tree expanded within Bound,
% if goal found then Solution is solution path and Solved = yes
% Case 1: goal leaf-node, construct a solution path
expand( P, l( N, _), _, _, yes, [N|P]) :-
goal(N).
% Case 2: leaf-node, f-value less than Bound
% Generate successors and expand them within Bound.
expand( P, l(N,F/G), Bound, Tree1, Solved, Sol) :-
F =< Bound,
( bagof( M/C, ( s(N,M,C), not(member(M,P)) ), Succ),
!, % Node N has successors
succlist( G, Succ, Ts), % Make subtrees Ts
bestf( Ts, F1), % f-value of best successor
expand( P, t(N,F1/G,Ts), Bound, Tree1, Solved, Sol)
;
Solved = never % N has no successors - dead end
) .
% Case 3: non-leaf, f-value less than Bound
% Expand the most promising subtree; depending on
% results, procedure continue will decide how to proceed
expand( P, t(N,F/G,[T|Ts]), Bound, Tree1, Solved, Sol) :-
F =< Bound,
bestf( Ts, BF), min( Bound, BF, Bound1), % Bound1 = min(Bound,BF)
expand( [N|P], T, Bound1, T1, Solved1, Sol),
continue( P, t(N,F/G,[T1|Ts]), Bound, Tree1, Solved1, Solved, Sol).
% Case 4: non-leaf with empty subtrees
% This is a dead end which will never be solved
expand( _, t(_,_,[]), _, _, never, _) :- !.
% Case 5: f-value greater than Bound
% Tree may not grow.
expand( _, Tree, Bound, Tree, no, _) :-
f( Tree, F), F > Bound.
% continue( Path, Tree, Bound, NewTree, SubtreeSolved, TreeSolved, Solution)
continue( _, _, _, _, yes, yes, Sol).
continue( P, t(N,F/G,[T1|Ts]), Bound, Tree1, no, Solved, Sol) :-
insert( T1, Ts, NTs),
bestf( NTs, F1),
expand( P, t(N,F1/G,NTs), Bound, Tree1, Solved, Sol).
continue( P, t(N,F/G,[_|Ts]), Bound, Tree1, never, Solved, Sol) :-
bestf( Ts, F1),
expand( P, t(N,F1/G,Ts), Bound, Tree1, Solved, Sol).
% succlist( G0, [ Node1/Cost1, ...], [ l(BestNode,BestF/G), ...]):
% make list of search leaves ordered by their F-values
succlist( _, [], []).
succlist( G0, [N/C | NCs], Ts) :-
G is G0 + C,
h( N, H), % Heuristic term h(N)
F is G + H,
succlist( G0, NCs, Ts1),
insert( l(N,F/G), Ts1, Ts).
% Insert T into list of trees Ts preserving order w.r.t. f-values
insert( T, Ts, [T | Ts]) :-
f( T, F), bestf( Ts, F1),
F =< F1, !.
insert( T, [T1 | Ts], [T1 | Ts1]) :-
insert( T, Ts, Ts1).
% Extract f-value
f( l(_,F/_), F). % f-value of a leaf
f( t(_,F/_,_), F). % f-value of a tree
bestf( [T|_], F) :- % Best f-value of a list of trees
f( T, F).
bestf( [], 9999). % No trees: bad f-value
min( X, Y, X) :-
X =< Y, !.
min( X, Y, Y).
% Starting positions for some puzzles
start1( [2/2,1/3,3/2,2/3,3/3,3/1,2/1,1/1,1/2] ). % Requires 4 steps
start2( [2/1,1/2,1/3,3/3,3/2,3/1,2/2,1/1,2/3] ). % Requires 5 steps
start3( [2/2,2/3,1/3,3/1,1/2,2/1,3/3,1/1,3/2] ). % Requires 18 steps
% An example query: ?- start1( Pos), bestfirst( Pos, Sol), showsol( Sol).